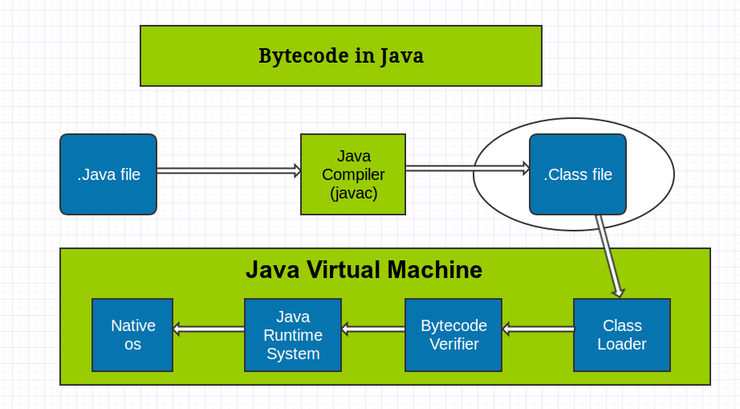
Explaination :
- Bytecode is computer object code that is processed by a program, usually referred to as a virtual machine, rather than by the "real" computer machine, the hardware processor.
- The virtual machine converts each generalized machine instruction into a specific machine instruction or instructions that this computer's processor will understand.
- Bytecode is the result of compiling source code written in a language that supports this approach.
- Most computer languages, such as C and C++, require a separate compiler for each computer platform - that is, for each computer operating system and the hardware set of instructions that it is built on.
- Windows and the Intel line of microprocessor architectures are one platform; Apple and the PowerPC processors are another.
- Using a language that comes with a virtual machine for each platform, your source language statements need to be compiled only once and will then run on any platform.
- The best-known language today that uses the bytecode and virtual machine approach is Java.
- The LISP language, used in artificial intelligence applications, is an earlier language that compiled bytecode. Other languages that use bytecode or a similar approach include Icon and Prolog.
- Rather than being interpreted one instruction at a time, Java bytecode can be recompiled at each particular system platform by a just-in-time compiler. Usually, this will enable the Java program to run faster. In Java, bytecode is contained in a binary file with a .CLASS suffix.
- Bytecode is the intermediate representation of Java programs just as assembler is the intermediate representation of C or C++ programs.
- The most knowlegable C and C++ programmers know the assembler instruction set of the processor for which they are compiling.
- This knowledge is crucial when debugging and doing performance and memory usage tuning.
- Knowing the assembler instructions that are generated by the compiler for the source code you write, helps you know how you might code differently to achieve memory or performance goals.
- In addition, when tracking down a problem, it is often useful to use a debugger to disassemble the source code and step through the assembler code that is executing.
- An often overlooked aspect of Java is the bytecode that is generated by the javac compiler.
- Understanding bytecode and what bytecode is likely to be generated by a Java compiler helps the Java programmer in the same way that knowledge of assembler helps the C or C++ programmer.
- The bytecode is your program.
- Regardless of a JIT or Hotspot runtime, the bytecode is an important part of the size and execution speed of your code.
- Consider that the more bytecode you have, the bigger the .class file is and the more code that has to be compiled by a JIT or Hotspot runtime.
- The remainder of this article gives you an in depth look at Java bytecode.

 August 06, 2017
August 06, 2017




